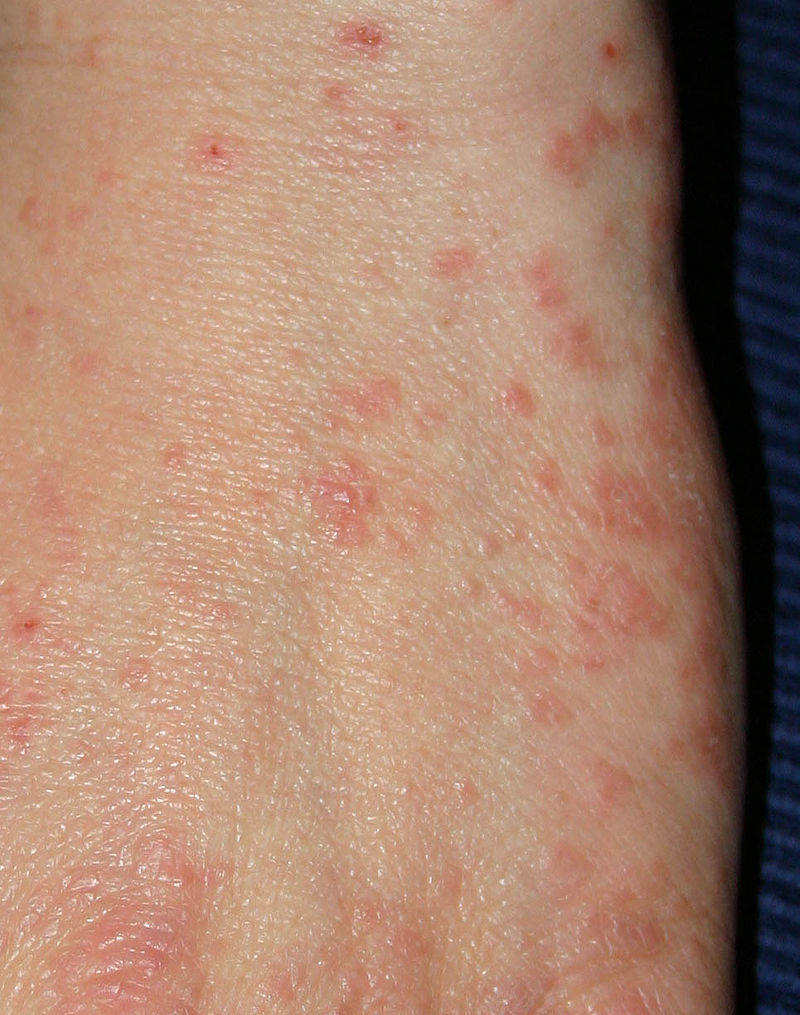
Lice and Scabies
Lice (Head, Body, and Genital)
Dx – must see the lice. Seeing nits alone does NOT diagnose, and is not an excuse for the kid to be out of school.
Rx – Permethrin 1% Shampoo. Leave on 10 min, then rinse. Repeat in 1 week to kill off any hatched eggs. Wash all clothes, bedsheets, towels with hot water. …
Continue reading
















Join the Discussion!