Anatomy Block 2
THINGS TO WATCH OUT FOR: EXCEPTIONS, COMPARISONS, ETC.
- Buccal Nerve vs. Buccal Branch of Facial Nerve
- Buccal Nerve comes off V3; Buccal Branch comes off Facial N.
- Buccal Nerve is Sensory; Buccal Branch of Facial is Motor.
- Three Muscles on Styloid Process:
- Stylopharyngeus – innervated by Glossopharyngeal N.
- Stylohyoid – innervated by Facial N. (remember stylohyoid is associated with Posterior Belly of Digastric M., which is also innervated by Facial N.)
- Styloglossus – innervated by Hypoglossal N.
- Stylopharyngeus – innervated by Glossopharyngeal N.
- Superior Laryngeal Nerve: Internal vs. ExternalBranches
- Internal Branch = sensory
- External Branch = Motor (innervates Cricothyroid)
- Cricothyroid vs. The Rest of LarynxInnervations:
- Cricothyroid = innervated by External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve.
- All other Laryngeal Muscles = innervated by Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve.
- Posterior vs. Anterior Belly of Digastric
- Posterior Belly = innervated by facial
- Anterior Belly = innervated by V3 (Nerve to Mylohyoid, to be exact – remember Anterior Belly is associated with Mylohyoid)
- Left vs. Right Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- Left = branches off Vagus, then loops around arch of aorta
- Right = branches off Vagus, then loops around Right Subclavian Artery
- Internal vs. External Jugular Veins:
- Internal = runs deep to Sternocleidomastoid
- External = runs superficial to Sternocleidomastoid
- Internal Jugular V and Internal Carotid A. vs. External Jugular V and External Carotid A
- Internal = goes straight up into brain
- External = goes outside of brain.
- Stapedius vs. Tensor Tympani:
- Facial N. → Stapedius → pulls on Stapes → dampens sounds (from voices)
- V3 → Tensor Tympani → pulls on malleus (which then pulls on tympanic membrane) → dampens sounds (from chewing).
- Components of Carotid Sheath:
- Internal Jugular Vein
- Common Carotid Artery
- Vagus Nerve runs between them.
- Genioglossus vs. Geniohyoid vs. MylohyoidInnervations:
- Genioglossus = innervated by Hypoglossal N. (XII)
- Geniohyoid = innervated by C1
- Mylohyoid = innervated by V3 (Nerve to Mylohyoid)
- Cranial Nerves that have Parasympathetic Innervation: CN 3, 7, 9, 10
- What does the Superior Oblique muscle do?
- Its action is to make your eye look down and out
- To test to see if the Superior Oblique works, look in and down (note: NOT down and in). Because the “out” action can also be done by lateral rectus, you can’t reliably test for Superior Oblique’s “out” function, and therefore you only test for the Superior Oblique’s “down” function. Because inferior rectus also does the “down” action, you tell the patient to look “in” first before looking “down” because inferior rectus doesn’t work well when the eye is adducted.
- Innervation of the Tongue:
-
Anterior 2/3 Posterior 1/3 General Sensation Lingual N. (from V3) Glossopharyngeal N. Taste Sensation Chorda Tympani (from Facial N.) Motor Hypoglossal N.
-
- Larynx Muscles:
- Only Abductor — Posterior Cricoarytenoid.
- Whispering Muscle (doesn’t adduct all the way) — Transverse Arytenoid M.
- Lowers pitch — Thyroarytenoid M.
- Raises pitch — Cricothyroid M.
- All “-glossus” muscles are innervated by hypoglossus except palatoglossus, which is innervated by vagus. All the pharynx muscles are vagus except stylopharyngeus, which is innervated by glossopharyngeus.
MNEMONICS
- Branches of Facial Nerve: Please Tell Ziggy Bob Marley Called.
- Please = Posterior Auricular
- Tell = Temporal Branch
- Ziggy = Zygomatic Branch
- Bob = Buccal Branch
- Marley = Mandibular Branch
- Called = Cervical Branch
- Cutaneous Branches of V1 (Ophthalmic Nerve): LIESS
- L = Lacrimal N.
- I = Infratrochlear N.
- E = Ethmoidal N.
- S = Supratrochlear N.
- S = Supraorbital N.
- Cutaneous Branches of V2 (Maxillary Nerve): ZIZ
- Z = Zygomaticotemporal N.
- I = Infraorbital N.
- Z = Zygomaticofacial N.
- Cutaneous Branches of V3 (Mandibular Nerve): BAM
- B = Buccal N.
- A = Auriculotemporal N.
- M = Mental N.
- Brances of Cervical Plexus: say “LOGATECS”
- LO = Lower Occipital N.
- GA = Great Auricular N.
- TC = Transverse Cervical N.
- S = Supraclavicular N.
- Branches of External Carotid Artery, from inferior to superior: Some Angry Lady Found Out PMS
- Some = Superior Thyroid A.
- Angry = Ascending Pharyngeal A.
- Lady = Lingual A.
- Found = Facial A.
- Out = Occipital A.
- P = Posterior Auricular A.
- M = Maxillary A.
- S = Superficial Temporal A.
- Nerves superior to orbit of eye – from medial to lateral – NFL:
- N = Nasociliary Nerve
- F = Frontal Nerve
- L = Lacrimal Nerve
- Layers of Scalp: SCALP
- S = Skin
- C = Connective Tissue
- A = Aponeurosis (more specifically, Galea Aponeurotica)
- L = Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
- P = Pericranium
- Remember “PS-FAMM-N” for the Drainages of the Nasal Meatus:
- Drainage to Superior Meatus: PS
- P= Posterior Ethmoidal Air Sacs
- S = Sphenoidal Sinus
- Drainage to Middle Meatus: FAMM
- F = Frontal Sinus
- A = Anterior Ethmoidal Air Sacs
- M = Middle Ethmoidal Air Sacs
- M = Maxillary Sinus
- Drinage to Inferior Meatus: N
- N = Nasolacrimal Duct
- Kiesselbach’s Area (Little’s Area) Anastomoses: FOMM
- F = Facial Artery (Superior Labial Branch)
- O = Ophthalmic Artery (Anterior Ethmoidal Branch)
- M = Maxillary Artery (Greater Palatine Branch)
- M = Maxillary Artery (Sphenopalatine Branch)
- Symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome: SPAM
- S = Sympathetic Chain impingement
- P = Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
- A = Anhydrosis (dehydration)
- M = Miosis (pin-point eye)
- Cranial Nerves — Are they Sensory, Motor, or Both? — Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More
- Some — CN I — Sensory
- Say — CN II — Sensory
- Marry — CN III — Motor
- Money — CN IV — Motor
- But — CN V — Both
- My — CN VI — Motor
- Brother — CN VII — Both
- Says — CN VIII — Sensory
- Big — CN IX — Both
- Brains — CN X — Both
- Matter — CN XI — Motor
- More — CN XII — Motor
- Cranial Nerve innervations of the Eye — LR6(SO4)3.
- LR6 — Lateral Rectus innervated by CN 6
- SO4 — Superior Oblique innervated by CN 4
- All other eye muscles innervated by CN 3
STRUCTURAL RELATIONSHIPS TO WATCH OUT FOR:
- Brachial Plexus emerges from between Anterior and Middle Scalene Muscles. Phrenic Nerve runs superficial to Anterior Scalene.
- Hypoglossal Nerve is deep to the Stylohyoid/Posterior Belly of Digastric.
- Vagus Nerve runs within the Carotid Sheath, which also includes common carotid artery, and internal jugular vein. The Carotid Sheath is deep to the Sternocleidomastoid.
- Posterior Belly of Digastric Muscle pierces through the Stylohyoid Muscle. Not too surprisingly, they are both innervated by Facial N.
- Ansa Cervicalis nerves = superficial to Carotid Sheath.
Vagus Nerve = inside Carotid Sheath.
Phrenic Nerve = deep to Carotid Sheath.
- The Auriculotemporal Nerve hugs the Middle Meningeal Artery.
- Facial vein and artery both travel up the face on the side of the nose.
SOME IMAGES TO MEMORIZE AND KNOW BY HEART:
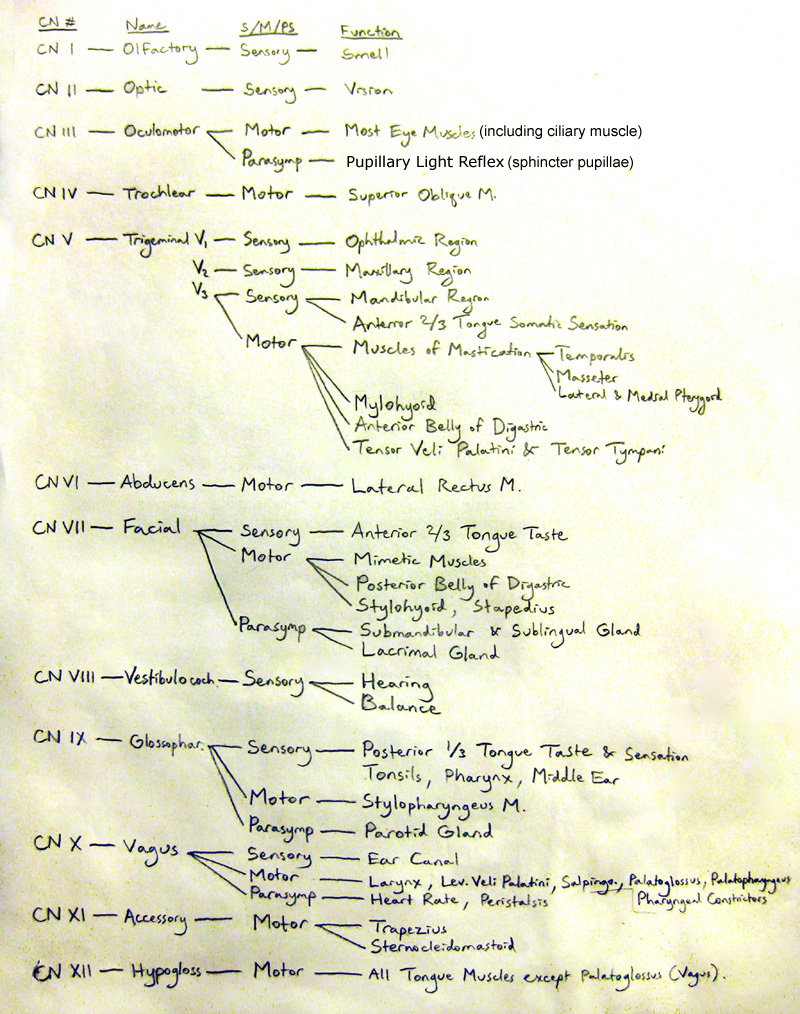
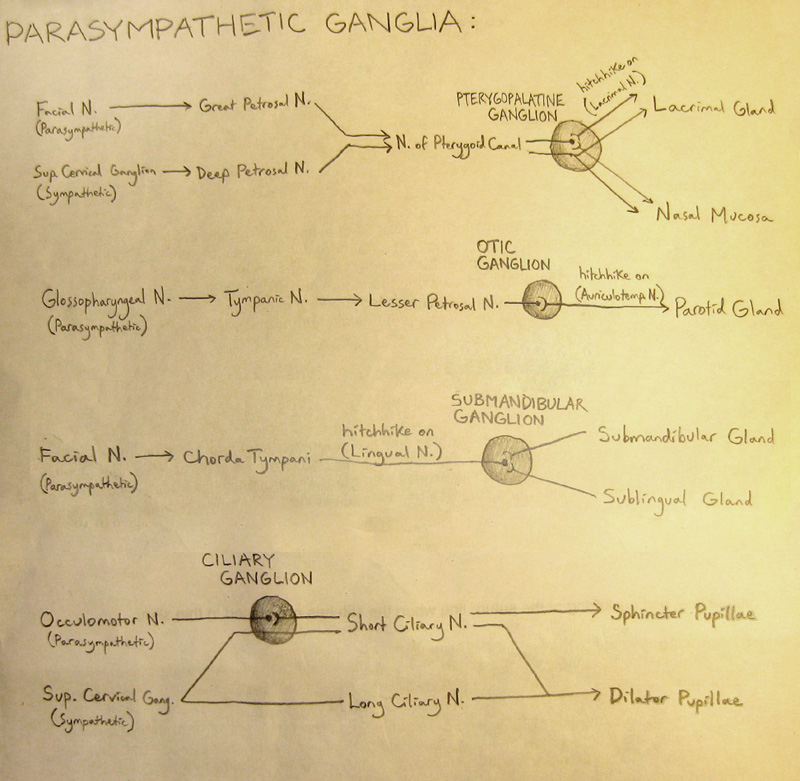
Can’t Remember the Cranial Nerves? Here’s a fun song I made that helped me remember! Play it a few times and it just might stick.









You have done well bro. Some invaluable mnemonic collection, especially for neurologists, ENT physicians. Keep it up.
Thanks man!
That is an amazing work u have done..made it easy to memorize
you are a life saver.thank you . june 2019
Is very helpfull thanks.